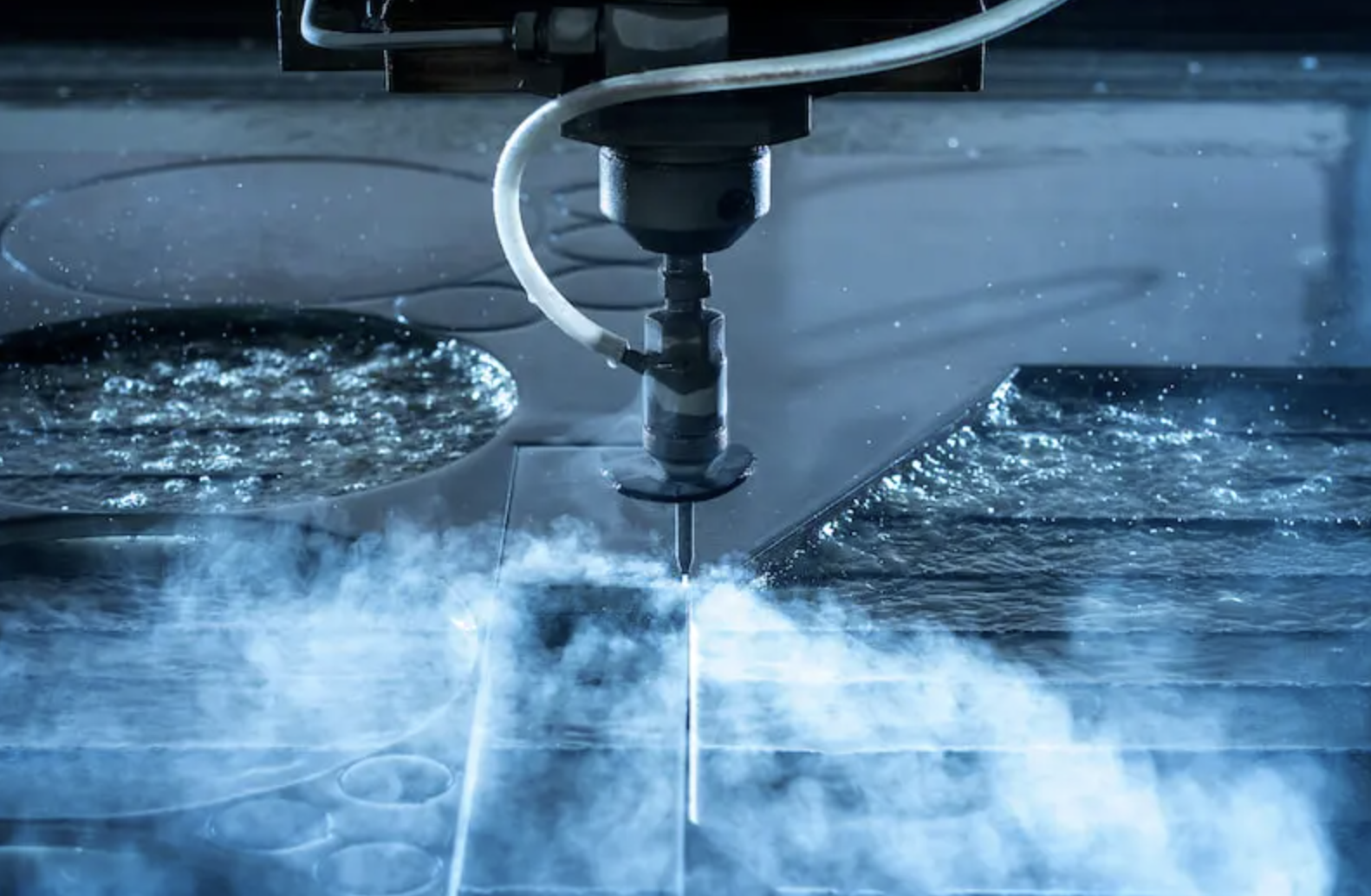
Waterjet cutting is a mechanical process where the material is removed by physical contact and material wear. The main difference with other cutting processes is the fact that it’s a cold-cutting process (non-thermal), meaning that no heat is used in the cutting process.
In today’s world, all manufacturing processes have to meet three main objectives: increase production, reduce waste and improve quality. Processes such as 3D printing, sheet forming, injection molding, laser and plasma cutting try to achieve these goals at reduced cost and production times while increasing efficiency and sustainability at the same time.
Every one of those processes has its place in the manufacturing industry due to various benefits and limitations. Modern waterjet cutters have also incorporated CNC technology into their design to meet these goals with even better results.
In this article, we shall take a deeper look into the advanced process of waterjet cutting.
What Is Waterjet Cutting?
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with an abrasive material to cut a wide range of materials.
A high-pressure water pump pressurizes the water. This water flows through high-pressure tubing into the cutting head. In the cutting head, the water flows through a nozzle, turning it into an extremely fine stream. This stream cuts whatever material is placed in front of it.
A waterjet cutting machine can produce pressures as high as 100,000 psi or about 6900 bars. To put it into perspective, fire hoses generally deliver pressures between 8 to 20 bars. The waterjet nozzle is assisted by a vision system to facilitate the precise and efficient cutting of the part.
It is easy to manipulate the nozzle to accommodate the cutting of different materials. Depending on whether an abrasive substance is used or not, there are two types of waterjet cutting methods:
- Abrasive waterjet cutting
- Pure waterjet cutting
Abrasive waterjet cutting
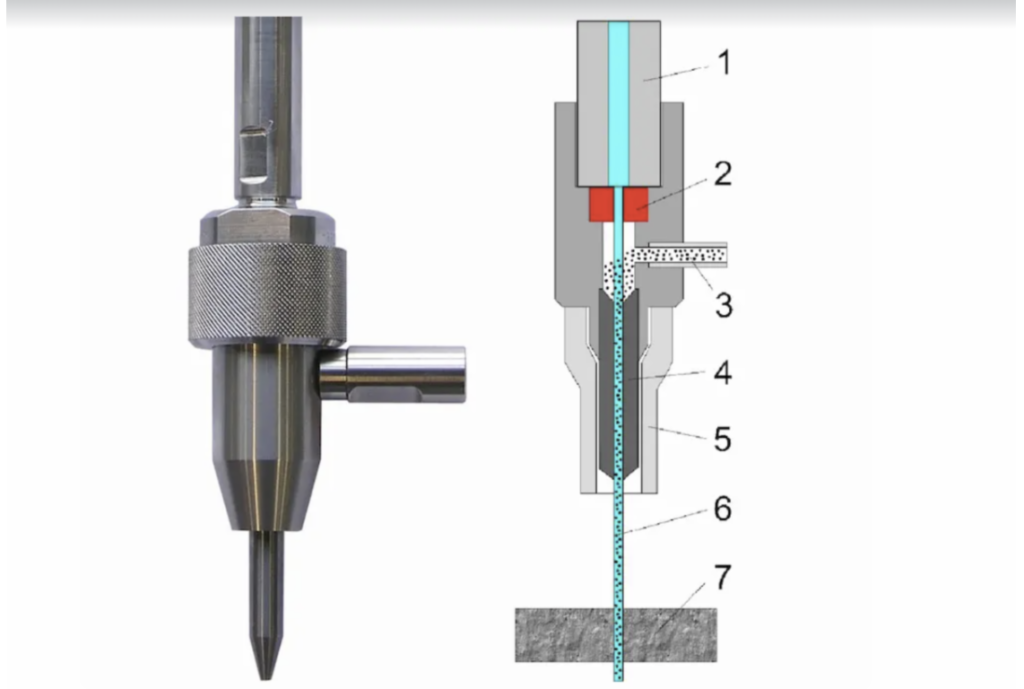
1. high-pressure water inlet; 2. jewel (ruby or diamond); 3. abrasive inlet; 4. mixing tube; 5. guard; 6. cutting water jet; 7. cut material
When cutting harder materials, abrasive agents are mixed with the water. This occurs in a mixing chamber located in the cutting head just before the abrasive jet exits the system.
Popular agents for abrasive waterjet cutting are suspended grit, garnet and aluminum oxide. As the material thickness/hardness increases, so should the hardness of the abrasives in use.
With the right abrasives, various material types can be cut. Common materials cut with abrasives are ceramics, metals, stones and thick plastics. There are, however, certain exceptions such as tempered glass and diamonds that cannot be cut with abrasive water. Tempered glass shatters when cut with a water jet.
Pure waterjet cutting
Water jet cutters also work without the addition of abrasives, mainly to cut soft materials. A waterjet cutter designed only for this purpose does not have a mixing chamber or a nozzle. A high-pressure pump forces pressurized water out of an orifice to create precise cuts on the workpiece. Although most industrial cutting devices using waterjet technology enable the use of both methods.
Pure waterjet cutting process is less invasive compared to abrasive waterjet cutting. The jet stream is also exceptionally fine and does not impart any additional pressure on the workpiece.
Pure waterjet cutting is ideal for softer materials like foam, felt, wood, rubber, food and thin plastics.
Waterjet Cutting Benefits
Waterjet cutting provides certain benefits that make it an excellent choice for general as well as very specific applications. Some of the benefits are as follows:
- High accuracy
- No heat-affected zone
- No need for tool changes
- Cost-effective process
- Compatibility with different materials
- Highly sustainable
High accuracy
Waterjet cutting is known for providing high cutting accuracy. Waterjet cut parts are of very high quality even when limited by tight specifications.
A water jet cutting machine can work with tolerances up to 0.025 mm (0.001 inches) but tolerances between 0.075 to 0.125 mm are more common for parts less than one inch in thickness.
The tolerances may increase with thicker materials depending on the technology. The accuracy depends on factors such as table stability, machine construction, abrasive flow rate, cutting stream control, stream lag, and process error.
No heat-affected zone
The heat-affected zone (HAZ) is a byproduct of most hot-cutting processes. In processes such as laser cutting and EDM, the zone around the cut edge does not melt during machining but undergoes a change in its properties.
Discoloration, heat distortion and hardened edges can all affect the characteristics of the final part. These parts require heat treatment before being put into use.
Being a cold-cutting process, waterjet cutting does not create heat-affected zones. This gives the final parts superior edge quality and more dependable properties without imparting any stress to the part.
The use of water jet cutting thus diminishes the need to worry about imperfect cuts, weak points and warping. Manufacturers can also use pre-heat treated parts to bring down production costs.
Being a non-thermal cutting process also means that there is no slag formation and dross waste created.
High-quality finished parts
Waterjet cutting delivers superior quality parts that no other cutting method can compete with. The edges are smooth and do not need deburring.
The final quality depends on several factors such as cutting speed, pressure, abrasive flow rate, and nozzle size. The process parameters may need to be modified for optimum output.
No need for tool changes
A waterjet cutter does not use any cutting tools and the nozzle does not need to be changed to accommodate different materials and thicknesses. The same nozzle is used for different applications by adjusting the cutting stream parameters, such as feed rate to achieve the appropriate cutting speed.
Since a tool change is not required between materials, the water jet cutting machine can cut different materials one after the other which improves the operational efficiency by saving time and tool costs.
Cost-effective process
Waterjet cutting is more cost-effective compared to alternative cutting methods in many applications, especially in the food industry. The process does not always need fixtures, jigs or clamps which increases the production speed.
Another benefit that this process offers is the possibility to stack and cut several layers of material all in one pass. Stacking can also be performed for dissimilar materials which makes this a simple yet effective way of increasing part production.
Cut parts also don’t require any post-processing which reduces the overall cost. The process also creates minimal material waste.
Compatibility with different materials
As explained before, the waterjet cutting process is not limited by the type of material. It can cut a wide range of materials as long as the correct process parameters and abrasives are selected. We shall cover this topic in detail further in the article.
Highly sustainable
In this day and age, sustainability is an important factor when selecting a manufacturing process. The waterjet-cutting process checks all the right boxes when it comes to sustainability. It has amazing advantages such as no slag formation, no dross waste, and no need for heated parts. It also does not create any toxic fumes or greenhouse gases.
The finished parts also do not require any post-processing tasks such as heat treatment. The main cutting medium of water is also recyclable which reduces the impact on the environment. In addition, no cooling oils or lubricants are required as the water jet itself acts as a coolant.

